What is trochanteric bursitis?
The two major fluid-filled sacs (bursae) located within the hip joint can become irritated and inflamed resulting in trochanteric bursitis. These bursae facilitate smooth and painless joint movement by reducing friction between the tissues as well as lubricating the surrounding joint structures. One of the hip bursae covers the greater trochanter of the femur, a bony prominence on the outer thigh bone, that is the attachment site for most of the major hip muscles. This trochanteric bursa is responsible for preventing inflammation of the attached muscles from the iliotibial (IT) band as it continuously slides back and forth over the greater trochanter. Trochanteric bursitis is a painful condition caused by blunt force trauma directly to the hip, repetitive hip motion, incorrect posture, previous surgery, or an underlying abductor (gluteus medius) tendon tear. There is research that has identified certain factors that can increase an individual’s risk of developing trochanteric bursitis: gender, age, gout, hip injury, and chronic hip pressure.
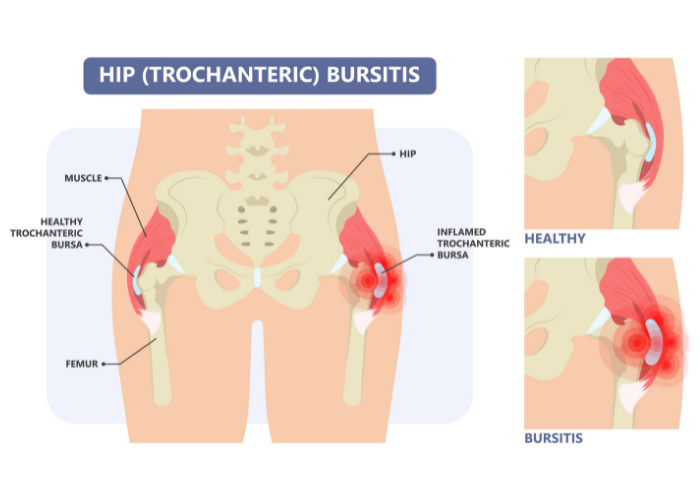
What is the treatment for trochanteric bursitis?
Non-surgical treatment measures alone are often able to alleviate symptoms in the majority of patients with trochanteric bursitis. These therapies include reducing physical activity, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory medications (NSAIDs), and a physical therapy program. However, some patients with more severe trochanteric bursitis symptoms may not respond well to non-surgical therapies. Surgical intervention to remove the damaged tissue may be necessary for these individuals. Dr. Ronak Mukesh Patel, orthopedic hip doctor, treats patients in Sugar Land, Pearland, and the Houston, Texas area, who have experienced trochanteric bursitis and are in need of a trochanteric bursectomy.
How is a trochanteric bursectomy performed?
Dr. Patel often performs a trochanteric bursectomy as an outpatient procedure as an overnight hospital stay is generally not warranted. After anesthesia has been administered, Dr. Patel makes a small incision on the side of the hip over the greater trochanter of the affected femur. Once the trochanteric bursa has been identified, the damaged tissue is excised and removed from the hip joint. Often times, there is an underlying abductor (gluteus medius) tendon tear than can be repaired sutures and anchors. If any other irregularities were documented, such as bone spurs or additionally inflamed tissue, they are addressed at this time. Even though a trochanteric bursectomy can be performed on its own, it can also be combined with other hip treatments such as iliotibial (IT) band release. When the necessary revisions have been completed, the arthroscope and surgical instruments are removed, and the incisions are closed with sutures or steri-strips.
How long is the recovery period after a trochanteric bursectomy?
The recovery period following a trochanteric bursectomy can be greatly affected by the patient’s willingness to follow the post-operative care instructions provided by Dr. Patel. Most patients can anticipate a full recovery with a return to normal daily and athletic activities in approximately 12 weeks. If a abductor tendon (gluteus medius) tendon repair is required, patients can expect to return to full activity in 5-6 months. Patients in the Houston, Texas area can typically expect the following:
- Walking and moving the hip as soon after surgery as possible or limited weight-bearing for 6 weeks if a tendon repair is required.
- A combination of rest, ice, and non-steroidal anti-inflammatory medications (NSAIDs) can be used to manage any post-operative pain and inflammation.
- The key to a successful recovery following a trochanteric bursectomy and/or abductor tendon repair is adhering to and completing the physical rehabilitation program prescribed by Dr. Patel. This physical therapy program will focus on gradual hip strengthening and improving range of motion while also being careful to protect the tissues as they heal.
Trochanteric Bursectomy Surgeon

Overuse of the hip, a fall, trauma to the hip or a previous surgery can result in a condition called trochanteric bursitis. In non-operative measures have failed to alleviate the symptoms of trochanteric bursitis, a minimally invasive procedure called an arthroscopic bursectomy may be used to remove or repair the damaged bursa tissue. Trochanteric bursectomy surgeon, Doctor Ronak Mukesh Patel, provides this specialized treatment option for patients in Houston, Sugar Land, and Pearland, TX who have trochanteric bursitis. Contact Dr. Patel’s team today!