What is a clavicle fracture?
The shoulder girdle consists of the clavicle (collarbone) and the scapula (shoulder blade). The clavicle is a horizontal S-shaped bone that acts as a strut between the scapula and sternum and is designed to oppose any forces bringing the upper limb toward the thorax. This is important as the range of motion of the upper limb relies on the clavicle to properly perform this function. The clavicle can be palpated just above the sternum and can easily be broken from a blunt force trauma such as a fall onto an outstretched arm or a direct blow to the shoulder girdle. Dr. Ronak Mukesh Patel, orthopedic shoulder specialist serving patients in Sugar Land, Pearland, and the Houston, Texas area, has the knowledge and understanding, as well as substantial experience, in treating patients with a clavicle fracture.
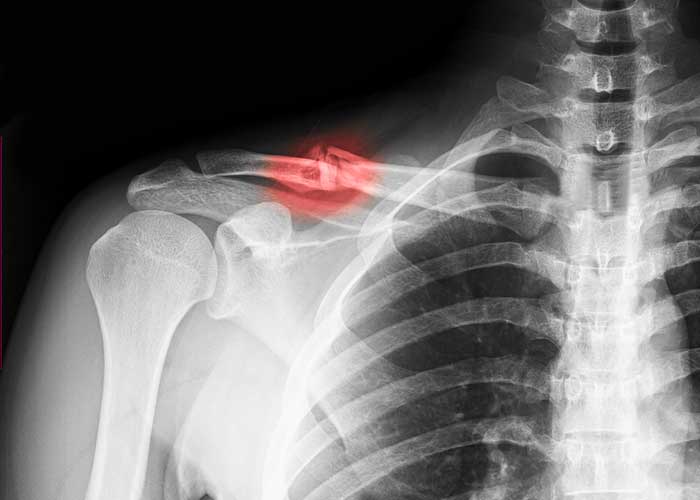
Are there different types of clavicle fractures?
There are three types of clavicle fractures that are named for the anatomical location of the fracture.
- Medial: The clavicle is fractured in the area closest to the neck. This is the least common type of clavicle fracture that accounts for only 2-4% of all clavicle fractures.
- Lateral/Distal: The clavicle is fractured at the point furthest away from the body’s midline near the top of the scapula. Surgical repair may be indicated contingent on bone placement.
- Midshaft: The clavicle is fractured in the middle portion along the bone shaft and is the most common type of clavicle fracture.
Are certain populations more at risk for a clavicle fracture?
A clavicle fracture is a common occurrence accounting for 5% of all adult bone fractures. Although this condition is predominantly the result of a traumatic event, there are certain populations that are more susceptible to clavicle fractures.
- Older Adults: Minor injuries can result in a clavicle fracture among older populations due to the natural decline in bone density with the aging process.
- Children and Teens: The bones of this population also have a lower density because they are still growing between the ages of 10 and 19.
- Athletes: Participants, especially males, in high-impact or aggressive contact sports have been shown to be three times more likely to sustain a clavicle fracture.
What are the symptoms of a clavicle fracture?
Symptoms of a clavicle fracture can vary, though patients that have sustained a clavicle fracture often report a sharp pain at the collarbone immediately following an injury. Other common complaints of a clavicle fracture can include:
- Obvious visual deformity of the clavicle
- Bruising, tenderness, and swelling surrounding the affected clavicle
- Downward shoulder sag
- Difficulty with lifting or rotating the affected arm
- Pain with arm movement
- Shoulder stiffness
How is a clavicle fracture diagnosed?
A detailed medical history, including the initial injury and any other related health conditions, will be obtained by Dr. Patel followed by a thorough physical examination. X-rays will then be conducted to confirm the diagnosis of a clavicle fracture. Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) and any additional diagnostic imaging may be performed to evaluate the other shoulder girdle structures, such as the labrum and rotator cuff, for any damage.
What is the treatment for a clavicle fracture?
Non-surgical treatment:
When there is no bone displacement from a clavicle fracture, patients may respond well to non-surgical therapies alone. The clavicle and affected arm are situated into the correct anatomical position and then immobilized by a sling or other device to prevent any further damage during the healing process. The pain and swelling associated with this condition can be managed by a combination of rest, ice application, and non-steroidal anti-inflammatory medications (NSAIDs). Restoration of shoulder girdle strength through a physical therapy program is encouraged when deemed appropriate by Dr. Patel.
Surgical treatment:
Surgical reconstruction of the clavicle is accomplished through open reduction and internal fixation (ORIF) with special plates, pins, and/or screws realigning the bone fragments into the correct anatomical arrangement. This treatment option is often necessary for patients with bone displacement, shortening of the clavicle fracture ends, a fracture that punctures through the skin, or when non-surgical therapies were unsuccessful.
Clavicle Fracture Specialist

Do you play contact sports, or participate in activities that may cause you to fall on an outstretched arm? If so, you may be at risk of sustaining a clavicle fracture. The clavicle, or collar bone, is one of the most common fractures seen in adults. Severe clavicle fractures may require surgery, while other collar bone breaks can heal on their own. Clavicle fracture specialist, Doctor Ronak Mukesh Patel, provides diagnosis as well as surgical and nonsurgical treatment options for patients in Houston, Sugar Land, and Pearland, TX who have suffered a clavicle fracture. Contact Dr. Patel’s team today!