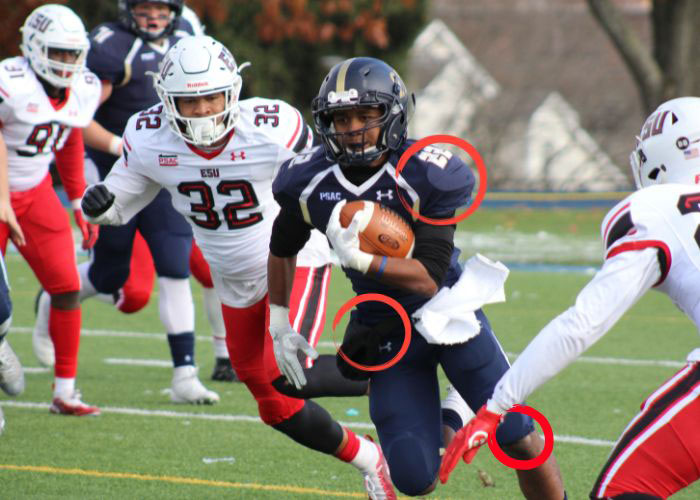
What is a knee cartilage injury?
Cartilage is a connective tissue that is found within all mobile joints in the body. This flexible yet firm tissue, when healthy, allows the ends of the bones to painlessly glide over one another during joint movement. The knee joint is home to two kinds of cartilage. Meniscus cartilage are two crescent-shaped discs found along the inner and outer portions of the knee that function as a shock absorber. Articular cartilage is a shiny and slippery white tissue that covers the lower end of the femur (thigh bone) and the upper end of the tibia (shin bone) where they join together to form the knee joint. Cartilage is generally a tough tissue but is still susceptible to damage and degeneration that can eventually cause knee joint pain and difficulty with walking. Dr. Ronak Mukesh Patel, orthopedic knee specialist serving patients in Sugar Land, Pearland, and the Houston, Texas area, has the knowledge and understanding as well as substantial experience in treating patients who have experienced a knee cartilage injury.
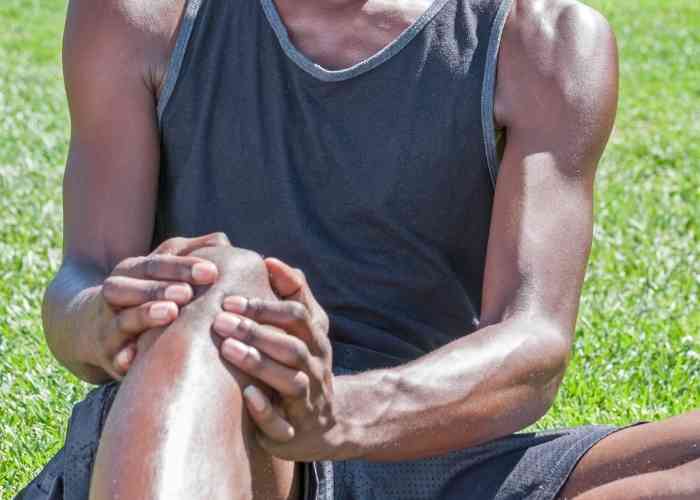

What causes a knee cartilage injury?
The knee cartilage can sustain damage from a traumatic event, work-related injury, chronic use of the knee joint, or a sports-related injury. Some specific events that can result in damage of the knee cartilage can include:
- Inflammation: In certain instances, the body’s own immune system can attack the knee cartilage resulting in inflammation and subsequent tissue degeneration.
- Dislocation: A traumatic event such as a football tackle or motor vehicle collision can force the knee joint out of its normal position.
- Infection: A penetrating injury, such as a dog bite, can transfer bacteria directly into the joint. Bacteria traveling through the bloodstream can also infiltrate into the knee joint and cause septic arthritis.
- Degeneration: The cartilage tissue can degenerate over time due to the normal aging process or from excessive grinding from structural abnormalities. If left untreated, this can eventually cause bone-on-bone joint movement.
- Cartilage Separation: Abnormal or violent twisting motions with the feet planted can result in the cartilage separating from the bone producing loose bodies within the knee joint.
- Meniscus Tear: The meniscus cartilage can become torn from a forceful knee rotation while bearing full body weight on the knee.
What are the symptoms of a knee cartilage injury?
Individuals report similar symptoms with knee cartilage injuries, regardless of which cartilage tissue is affected. Some common symptoms of a knee cartilage injury can include:
- A “locking” or “catching” sensation
- Abnormal gait or difficulty walking
- Decreased range of motion
- Intense and sharp pain at the time of injury, or a dull ache that gradually worsens with time
- Joint inflammation and swelling that is more noticeable after activity
How is a knee cartilage injury diagnosed?
Dr. Patel will gather a complete medical history followed by performing a thorough physical examination of the affected lower extremity. Diagnostic imaging studies, such as weight-bearing x-rays and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), can be useful for analyzing the cartilage damage and identifying damage to any of the other soft tissue structures within and surrounding the knee joint.
What is the treatment for a knee cartilage injury?
Non-surgical treatment:
Conservative therapies may be beneficial for certain patients based on the severity, location, and type of cartilage damage sustained. A combination of rest, ice, and non-steroidal anti-inflammatory medications (NSAIDs) are encouraged for pain and inflammation management. If these symptoms still persist with oral medications, a corticosteroid injection or other biologic treatment can be delivered directly into the knee joint. A physical therapy program can also be useful for healing by improving joint flexibility and strengthening the surrounding muscles.
Surgical treatment:
However, surgical intervention may be required in the event of failed conservative therapy or a severe and complex knee cartilage injury. Dr. Patel will account for the patient’s age, activity level, medical history, type of injury, and severity of damage when formulating the appropriate treatment plan. A simple debridement procedure involving the removal of the damaged cartilage fragments may be suitable for patients with mild knee cartilage injuries. Focal articular cartilage defects often respond well to cartilage restoration or transplantation surgery. A cartilage graft, either from the patient (autograft) or donor (allograft), can also be molded and fastened to the patient’s specific cartilage defects.
Cartilage Injury Specialist

Athletes who participate in contact sports have a high risk of sustaining a knee cartilage injury. Cartilage injuries are often caused by trauma, contact sports, repetitive weight bearing, and age related degeneration. Knee cartilage injury specialist, Doctor Ronak Mukesh Patel, provides diagnosis as well as surgical and nonsurgical treatment options for patients in Houston, Sugar Land, and Pearland, TX who have suffered a cartilage injury. Contact Dr. Patel’s team today!