Schedule an Appointment with a Hip Labrum Specialist
If you believe you are suffering from an acute labral tear requiring an urgent appointment, we will do our best to provide a same-day or next business day appointment.

If you participate in sports or activities that involve repetitive twisting movements, you may be at an increased risk of experiencing a hip labral tear. The hip labrum is a fibrocartilaginous tissue lining the joint between the femur and pelvis. Injuries to this tissue result in pain, instability when standing or moving, and a “locking” sensation with movement. Board certified complex hip specialist Doctor Ronak Mukesh Patel diagnoses and treats patients in Houston, Sugar Land, and Pearland, TX who have experienced an injury to the hip labrum. Contact Dr. Patel’s team for an appointment today!
What is the acetabular labrum of the hip?
The hip joint is formed into a ball-and-socket arrangement from the articulation of the head of the femur (thigh bone) into the socket portion of the acetabulum (pelvis). Lining the socket of the acetabulum is a fibrocartilaginous tissue, known as the acetabular hip labrum, that creates a seal between the femoral head and the pelvis. Even though the hip labrum does supply some joint lubrication, its primary responsibility is to restrict femoral head movement by securing the ball of the femoral head in place to provide a suction seal effect. The hip labrum also provides joint stability by deepening the acetabular socket and serves as a shock absorber by equally distributing the stresses loaded onto the hip joint.
What causes a hip labral tear?
A tear to the acetabular labrum can occur by a number of different mechanisms. Structural abnormalities are the most common causes of hip labrum tears. For example, femoroacetabular impingement (hip FAI) is often accompanied by labral tears due to “bumping” between a misshapen femoral head and/or deep acetabular socket. Leaving the underlying conditions untreated can result in excessive wear and tear of the hip acetabular labrum and cartilage causing pain and is associated with the progression of osteoarthritis.
Hip instability is also an increasingly recognized cause of labral tears. Dysplasia is a condition where the acetabulum (hip socket) is shallow from birth. This leads to microinstability of the hip leading to a labral tear. However, more commonly some females who are hypermobile (“double-jointed”) may also have hip instability without frank dysplasia. This is a more common cause of labral tears and hip pain that we are seeing. The treatment depends on a number of factors including the history, exam, and imaging findings.
Other health conditions that cause the hip cartilage to break down or weaken can increase an individual’s likelihood of a hip labral tear. Athletes are also at a higher risk of tearing the hip labrum, especially those that perform repetitive twisting or pivoting motions frequently seen in football, hockey, soccer, golf, skating, ballet or dancing. However, hip labral tears are also seen in adults actively involved in running and weight-lifting. Dr. Ronak Mukesh Patel, orthopedic hip specialist serving patients in Sugar Land, Pearland, and the Houston, Texas area, has substantial experience in treating patients who have experienced a hip labral tear.
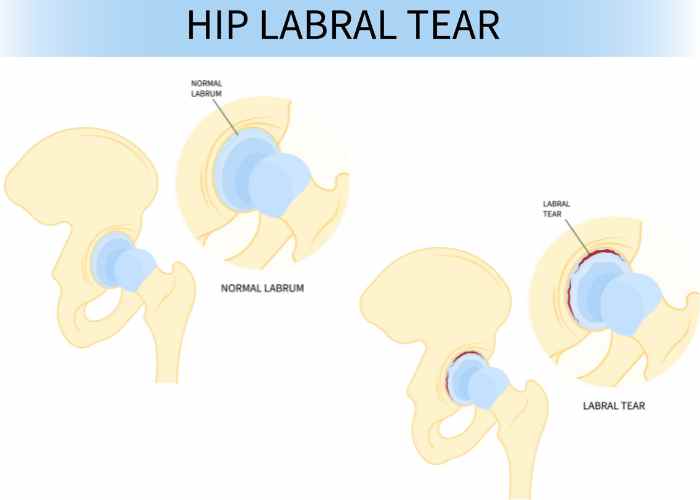
What are hip labral tear symptoms?
The most common complaint of a hip labral tear is hip pain or stiffness that may worsen with certain hip movements or athletic activities. Surprisingly, some individuals do not report any symptoms from a torn acetabular labrum at all. Some other common complaints of a hip labral tear can include:
- Pain in the hip around the front, groin, or side area
- Hip tightness or stiffness
- A “locking” or “clicking” sound with hip movement
- Pain with walking or running
- Pain with sitting or driving
- Feeling unsteady on one’s feet or hip giving out
Is there a specific hip labral tear test or how is a torn hip labrum diagnosed?
Provocative hip labral tear tests can be useful in diagnosing hip labral tears but need to be considered in context with other information gathered from a patient. Dr. Patel will assess the following during the initial patient consultation:
- Comprehensive medical history. Patient typically describe pain in the front/groin and side of the hip with a deep feeling. The pain is worse with activity, sitting for long periods, driving, and squatting.
- Physical examination of the hip to test for pain and range of motion of the affected hip. Pain is typically with hip flexion (knee brought to chest) and with the impingement test where the hip is flexed, adducted and internally rotated (FADIR) with pain reproduced.
- Diagnostic imaging studies, such as x-rays and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI). Xrays are evaluated to examine for hip arthritis, impingement, fractures, etc. MRI is used to evaluate the labrum, cartilage, tendons, ligaments and bones.
- Diagnostic and therapeutic injections are essential for the diagnosis and treatment of labral tears. We know that labral tears on MRI are very common. Injections are done in the hip joint under ultrasound guidance in the office. If the injection provides relief of symptoms, even for a short period of time, this would indicate that the labral tear is the source of pain.
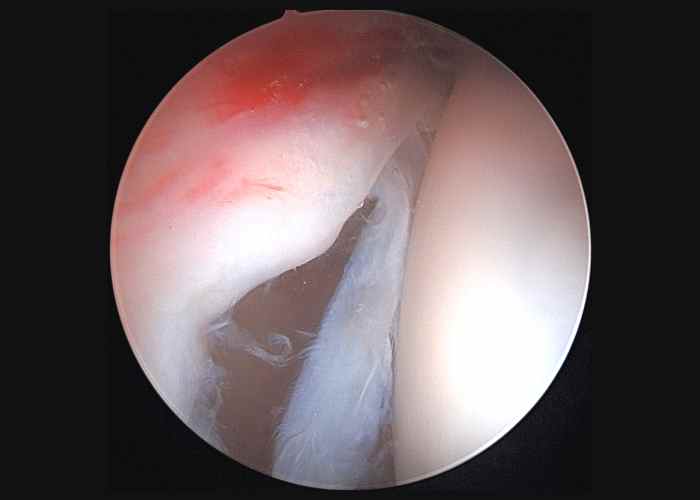
What is the treatment for a hip labral tear?
Hip labral tear recovery without surgery
Most hip labral tears do not require surgery. Although a hip labral tear is not likely to spontaneously resolve, patients with a hip labrum tear may find relief without surgery through non-surgical treatment measures. A combination of resting the hip joint, modifying activities, and non-steroidal anti-inflammatory medications (NSAIDs) may be beneficial in managing the pain and inflammation associated with this condition. If these symptoms still persist with oral medications, a corticosteroid or platelet-rich plasma (PRP) injection can be administered directly into the hip joint. Dr. Patel will prescribe a specialized physical rehabilitation program that focuses on strengthening and stretching the hip and core muscles.
Hip labral tear surgery
If a patient does not respond well to non-surgical treatment measures, surgical intervention is likely necessary to restore the original function of the hip labrum for joint stabilization. Hip labrum repair surgery is often performed through a minimally invasive arthroscopic procedure involving a small camera (arthroscope) and specialized surgical instruments. There are different surgical approaches that Dr. Patel can employ to successfully repair the hip labrum. Debridement involves excising and removing the damaged portions of the hip labrum. The remaining healthy tissue can then be sutured back together and reattached to the bone. A complex hip labrum tear or small (hypoplastic or deficient) labrum may require a labral reconstruction with a tissue graft from a donor (allograft), to reconstruct the hip labrum entirely. Femoroacetabular impingement (FAI), if present, will also be surgically addressed to prevent a hip labrum tear in the future and improve hip mechanics.