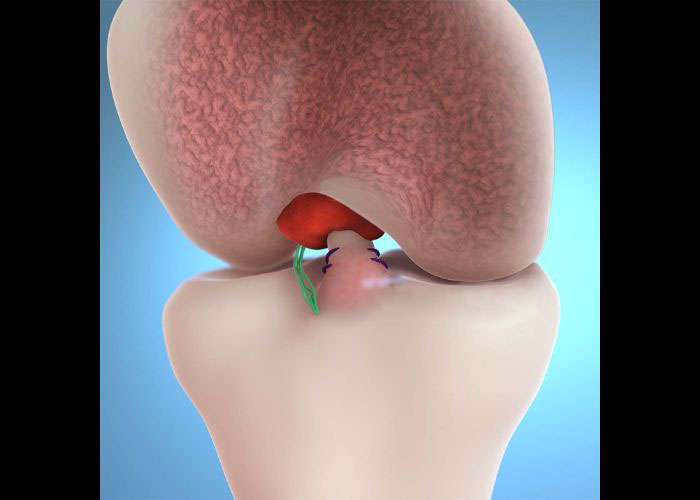
What is a patella dislocation?
The patella (kneecap) is a sesamoid bone that is found at the articulation point of the femur (thigh bone) and tibia (shin bone). This bone is anchored in place by the quadriceps tendon, attached to the femur, and the patellar tendon, attached to the tibia. The patella can become dislodged by a traumatic blow to the knee, a shallow trochlear groove, an anatomical abnormality such as a high-riding patella or lateralized insertion of the patellar tendon on the tibial tubercle, or weakened ligaments from prior patella dislocations. Severe patella dislocations often result in more complex and extensive damage to the surrounding soft-tissue structures and cartilage.
What is the treatment for a patella dislocation?
Patients who sustain mild ligament injuries from a patella dislocation often respond well to non-surgical therapies such as rest, ice, and non-steroidal anti-inflammatory medications (NSAIDs). However, surgical intervention may be necessary for failed non-surgical therapy, extensive or complex knee injuries, or damage to multiple knee joint structures. There are several surgical techniques that can be implemented to restabilize the patella. Because the ligament structure is disrupted in a patella dislocation event, surgery is the best treatment option to prevent future patella dislocations. Dr. Ronak Mukesh Patel, orthopedic knee doctor, treats patients in Sugar Land, Pearland, and the Houston, Texas area, who have experienced a patella dislocation and are in need of surgical repair.
How is a kneecap dislocation surgery performed?
There are a number of various surgical procedures that can be performed to correct a patella dislocation. Dr. Patel will take the patient’s age, activity level, medical history, specific injury, and desired recovery outcomes into consideration when designing each patient’s treatment plan. The following are some of the surgical procedures that Dr. Patel may perform for a patella dislocation:
- Lateral Retinaculum Release: The lateral retinaculum is a fibrous tissue found on the outer patella. Releasing this tissue can alleviate tension on the outer knee and realign the kneecap. This procedure is a common surgical treatment for patients with patellar instability or a partially dislocated (subluxated) patella.
- Trochleoplasty: This method is performed as an open surgery where a new groove is reshaped into the distal femur for the patella. Patients with severe patellar instability are good candidates for this surgical technique.
- MPFL Reconstruction: This minimally invasive procedure reconstructs the medial patellofemoral ligament (MPFL) by excising and removing the damaged tissue fragments and suturing the remaining healthy tissue back together. A tissue graft may be implemented from the patient (autograft) or donor tissue (allograft) if there is not enough of the original ligament remaining.
- Medial Imbrication: The goal of medial imbrication, also known as reefing, is to tighten the tissue on the inner side of the knee. This method is often performed with other procedures in the knee.
- Tibial Tubercle Osteotomy: Patients that experience recurrent patella dislocations from a shallow trochlear groove will undergo this surgical procedure. The tibial tubercle (bony prominence of the shin bone) is extracted with the patellar tendon still attached and transferred to another position on the tibia. Correcting this abnormal lower extremity alignment results in the patella being pulled inward.
What is the recovery period like after a kneecap dislocation surgery?
The recovery period following a kneecap dislocation surgery is largely determined by the specific surgical technique implemented by Dr. Patel. While some patients may recover in 4 to 5 months, most patients can expect a full recovery in approximately 8 to 12 months. The patient’s willingness to comply with the post-operative care instructions set forth by Dr. Patel can also greatly affect the recovery process. Patients in the Houston, Texas area can anticipate the following:
- The knee will be immobilized with a brace or other medical device immediately following surgery.
- Weight-bearing is limited with the assistance of crutches or a walker. Patients that undergo a tibial tubercle osteotomy should avoid weight-bearing entirely for at least 6 weeks to allow the bone to heal.
- Post-operative pain and inflammation can be managed with a combination of rest, ice, elevation, and non-steroidal anti-inflammatory medications (NSAIDs).
- A regimented physical rehabilitation program will be tailored according to the kneecap dislocation surgery that was performed. The key to a successful recovery is active participation and completion of this physical therapy program.
- A strict physical rehabilitation program will be tailored based on the articular cartilage restoration technique performed. The key to a successful recovery following articular cartilage restoration is adhering to and completing this physical therapy program.
Patella Dislocation Surgeon

Activities that require rapid changes of direction can cause the knee to twist inappropriately and the patella (kneecap) to dislocate. Patients who experience this frequently may have a condition called luxating patella. Severe or continued patella dislocations may require surgery to stabilize the knee and eliminate pain. Patella dislocation surgeon, Doctor Ronak Mukesh Patel, provides diagnosis as well as surgical and nonsurgical treatment options for patients in Houston, Sugar Land, and Pearland, TX who have suffered a patella dislocation and require surgery. Contact Dr. Patel’s team today!