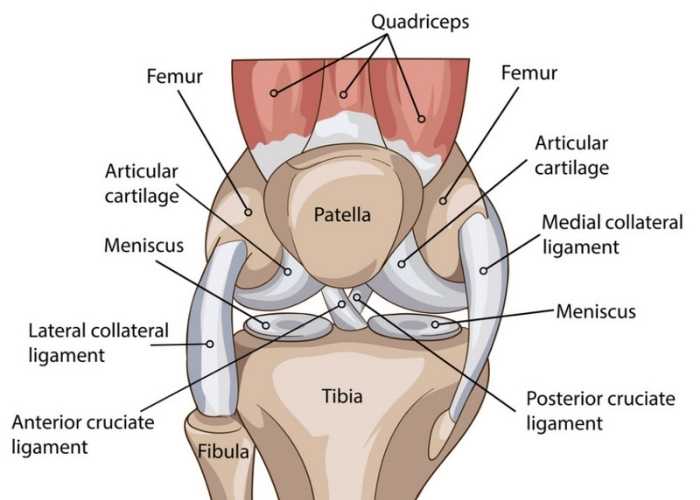
Knee
Recent Articles & News
Locations
Fondren Orthopedic Group – Sugar Land
13440 University Blvd, Suite 100
Sugar Land, TX 77479
Fondren Orthopedic Group – Pearland
10223 Broadway St, Suite A
Pearland, TX 77584
Fondren Orthopedic Group – Houston
7401 Main St
Houston, TX 77030
DISCLAIMER
All information contained on the houstonsportsortho.com website is intended for informational and educational purposes. The information is not intended nor suited to be a replacement or substitute for professional medical treatment or for professional medical advice relative to a specific medical question or condition. (Website Terms & Conditions | Privacy)
Copyright © Ronak Mukesh Patel, MD All Rights Reserved